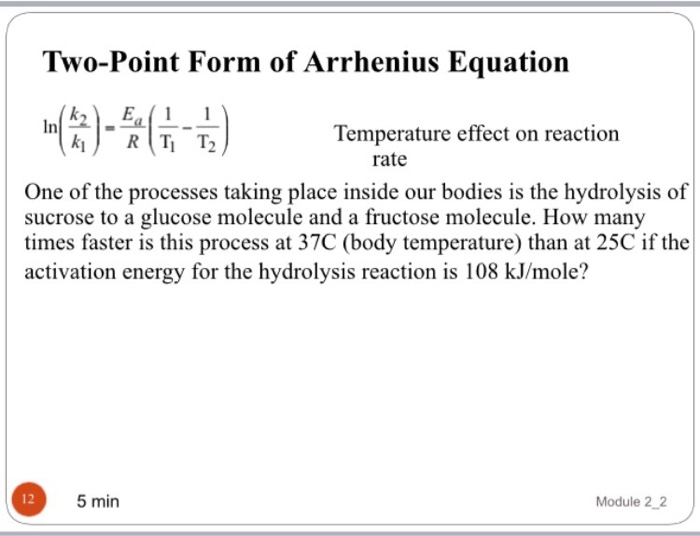
Two Point Form Of Arrhenius Equation
Two Point Form Of Arrhenius Equation - E a is the activation energy of the reaction (usually given in joules per mole or j/mol) Web the arrhenius equation as it's used in chemistry is often stated according to the formula: K = ae − ea / rt. Can be visualised as the frequency of correctly oriented collisions between reactant particles). A is an exponential factor that is a constant for a given chemical reaction, relating the frequency of collisions of particles. Web forms of the arrhenius equation (video) | khan academy.
The activation energy equation using the arrhenius formula is: K = ae − ea / rt. Want to join the conversation? A is an exponential factor that is a constant for a given chemical reaction, relating the frequency of collisions of particles. Web the arrhenius equation can be used to determine the effect of a change of temperature on the rate constant, and consequently on the rate of the reaction.
This gives less accurate values for e a, but is computationally quicker. On rearranging the equation, an expression for the activation energy is generated. 126 views 5 years ago general chemistry. The slope of the arrhenius plot can be used to find the activation energy. If we know the rate constants at two temperatures, then the activation energy can be found.
Web the arrhenius equation gives the dependence of the rate constant of a chemical reaction on the absolute temperature as. If we look at the equation that this arrhenius equation calculator uses, we can try to understand how it works: Web the arrhenius equation is a formula that describes how the rate of a reaction varied based on temperature, or.
Web the arrhenius equation as it's used in chemistry is often stated according to the formula: The arrhenius equation for the activation energy of a chemical reaction, especially its two point form, is an intimidating looking beast. It provides insight into the dependence of. This gives less accurate values for e a, but is computationally quicker. Web the arrhenius equation,.
Web the arrhenius equation relates the activation energy and the rate constant, k, for many chemical reactions: Using the arrhenius equation to look at how changing temperature and activation energy affects collisions. Web the arrhenius equation can be used to determine the effect of a change of temperature on the rate constant, and consequently on the rate of the reaction..
Web the arrhenius equation can be used to determine the effect of a change of temperature on the rate constant, and consequently on the rate of the reaction. Using the arrhenius equation to look at how changing temperature and activation energy affects collisions. By substituting any two data pairs and further calculation yields the value for the activation energy in.
Can be visualised as the frequency of correctly oriented collisions between reactant particles). A is an exponential factor that is a constant for a given chemical reaction, relating the frequency of collisions of particles. It provides insight into the dependence of. Substracting equation (4) from equation (3) results in rerrangement of equation (5) and solving for e a yields The.
Substracting equation (4) from equation (3) results in rerrangement of equation (5) and solving for e a yields If the rate constant doubles, for example, so does the rate of the reaction. Can be visualized as the frequency of correctly oriented collisions between reactant particles). Web the arrhenius equation as it's used in chemistry is often stated according to the.
Web the arrhenius equation gives the dependence of the rate constant of a chemical reaction on the absolute temperature as. Web arrhenius derived a simple relationship between rate constant k and temperature of the reaction system, which is called as arrhenius equation. 1.1k views 3 years ago general. Want to join the conversation? E a is the activation energy of.
Two Point Form Of Arrhenius Equation - Web arrhenius derived a simple relationship between rate constant k and temperature of the reaction system, which is called as arrhenius equation. A is an exponential factor that is a constant for a given chemical reaction, relating the frequency of collisions of particles. E a is the activation energy of the reaction (usually given in joules per mole or j/mol) Lnk = ln(ae − ea / rt) = lna + ln(e − ea / rt) = (− ea r)(1 t) + lna. If we know the rate constants at two temperatures, then the activation energy can be found. If we look at the equation that this arrhenius equation calculator uses, we can try to understand how it works: If the rate constant doubles, for example, so does the rate of the reaction. 1.1k views 3 years ago general. Web the arrhenius equation gives the dependence of the rate constant of a chemical reaction on the absolute temperature as. The activation energy equation using the arrhenius formula is:
Web arrhenius derived a simple relationship between rate constant k and temperature of the reaction system, which is called as arrhenius equation. Lnk = ln(ae − ea / rt) = lna + ln(e − ea / rt) = (− ea r)(1 t) + lna. Web two point form of the arrhenius equation? The slope of the arrhenius plot can be used to find the activation energy. Web k = ae−ea rt (6.2.3.4.1) (6.2.3.4.1) k = a e − e a r t.
Web the arrhenius equation is a formula that describes how the rate of a reaction varied based on temperature, or the rate constant. K = ae − ea / rt. Web the arrhenius equation, k = ae − ea / rt. Web the arrhenius equation can be used to determine the effect of a change of temperature on the rate constant, and consequently on the rate of the reaction.
On rearranging the equation, an expression for the activation energy is generated. Web the arrhenius equation, k = ae − ea / rt. The arrhenius equation for the activation energy of a chemical reaction, especially its two point form, is an intimidating looking beast.
Web k = ae−ea rt (6.2.3.4.1) (6.2.3.4.1) k = a e − e a r t. Web the arrhenius equation as it's used in chemistry is often stated according to the formula: How to write different forms of the arrhenius equation.
Web The Arrhenius Equation Is A Formula That Describes How The Rate Of A Reaction Varied Based On Temperature, Or The Rate Constant.
Web arrhenius derived a simple relationship between rate constant k and temperature of the reaction system, which is called as arrhenius equation. This gives less accurate values for e a, but is computationally quicker. Web k = ae−ea rt (6.2.3.4.1) (6.2.3.4.1) k = a e − e a r t. If we know the rate constants at two temperatures, then the activation energy can be found.
Web The Arrhenius Equation Can Be Used To Determine The Effect Of A Change Of Temperature On The Rate Constant, And Consequently On The Rate Of The Reaction.
On rearranging the equation, an expression for the activation energy is generated. Web the arrhenius equation, k = ae − ea / rt. Using the arrhenius equation to look at how changing temperature and activation energy affects collisions. Web forms of the arrhenius equation (video) | khan academy.
Web The Arrhenius Equation Relates The Activation Energy And The Rate Constant, K, For Many Chemical Reactions:
Can be visualised as the frequency of correctly oriented collisions between reactant particles). The slope of the arrhenius plot can be used to find the activation energy. How to write different forms of the arrhenius equation. Web the arrhenius equation as it's used in chemistry is often stated according to the formula:
Web The Arrhenius Equation Gives The Dependence Of The Rate Constant Of A Chemical Reaction On The Absolute Temperature As.
The arrhenius equation for the activation energy of a chemical reaction, especially its two point form, is an intimidating looking beast. Can be visualized as the frequency of correctly oriented collisions between reactant particles). K = ae − ea / rt. A is an exponential factor that is a constant for a given chemical reaction, relating the frequency of collisions of particles.