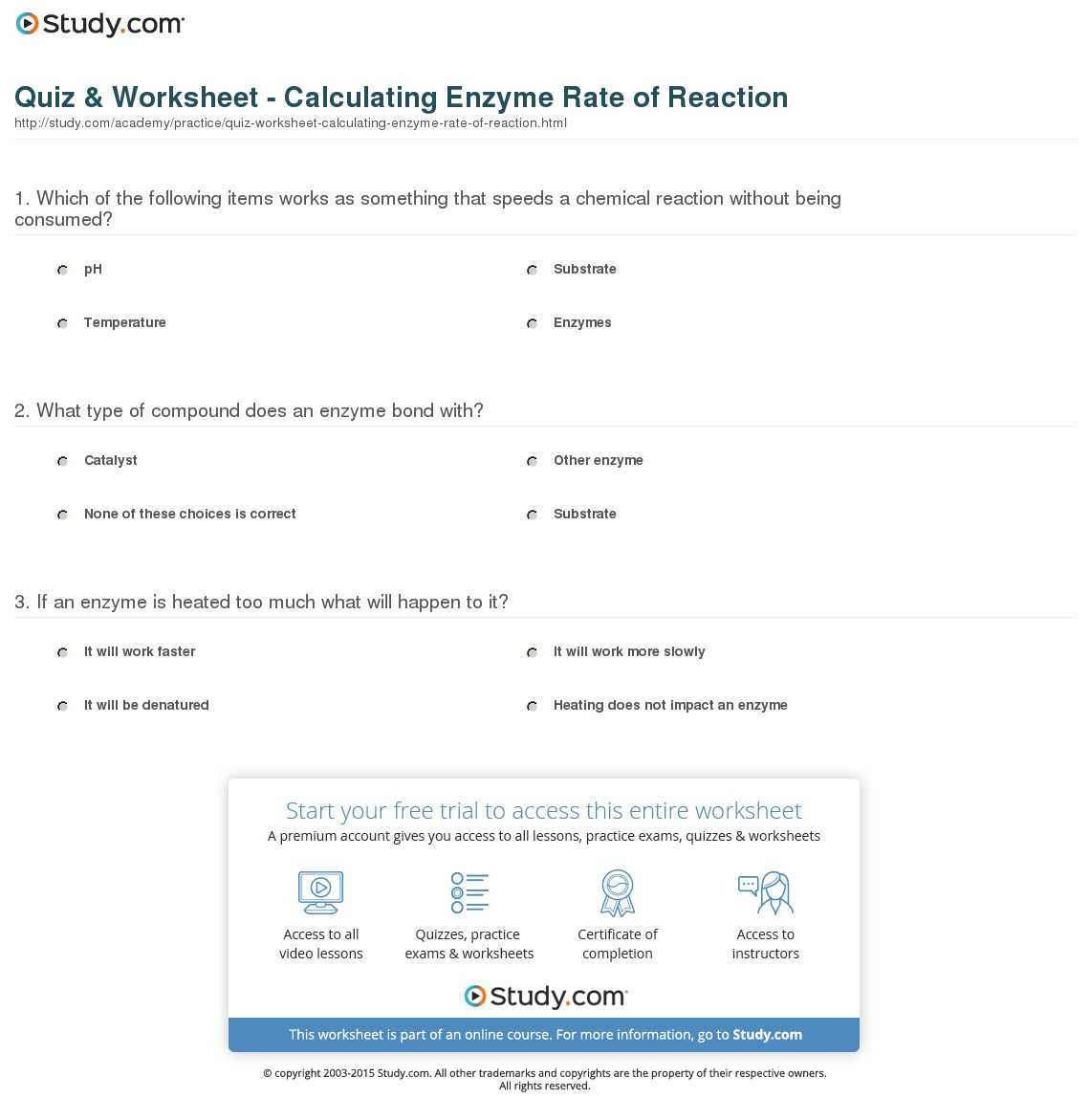
Reaction Rates Worksheet
Reaction Rates Worksheet - How will the rate change if the concentration of a is halved? Designed as an introduction only:this product is designed to be used as an introd. I have used other people's resources for one of the questions, thanks to them. Example questions from the worksheet: Ii higher the concentration, the faster the reaction. Reaction rate the speed at which a chemical reaction proceeds.
Web a range of worksheets, with answers, to help pupils to revise aspects of rates of reaction, including: A reaction has the experimental rate law, rate = k[a]2. Reaction rate the speed at which a chemical reaction proceeds. Catalyst a substance that causes or accelerates a chemical reaction without itself being affected. All your revision in one place.
Includes answers for marking in class. Web worksheets are name per work reaction rates, chemistry 12 work 1 1, work reaction rates name, types of reactions work, chapter 16 reaction rates, science term 1 rates of reaction, reaction rates and chemical equilibrium, sample exercise calculating an average rate of reaction. (1) temperature, (2) particle size, and (3) concentration of the reactants. Worksheets and lesson ideas to challenge students to think hard about rates of reaction, graphs and collision theory (gcse and key stage 3) rates of reaction is a rich topic area for practicals that students really enjoy. Web a range of worksheets, with answers, to help pupils to revise aspects of rates of reaction, including:
Web a student investigated the rate of reaction between calcium carbonate (marble chips) and hydrochloric acid. Topics include collision theory, particles, factors that affect rate and reaction profiles/energy level diagrams with a variety of questions and challenging calculations. Rates of reaction, collision theory, effect of variables on reaction rates including temperature, concentration, pressure, surface area, catalysts, and inhibitors.note: Web a.
If a reaction is to occur, reacting particles must first _____ and this _____ must be effective. Web a revision homework or class worksheet with answers that covers rates of reaction in c6 gcse chemistry. According to the collision theory, what 3 circumstances are needed for c6h12o6 & o2 to react? B i a + c. Worksheets and lesson ideas.
Web to summarise, the rate of reaction can be affected by: Web calculating rates of reaction. Web rates of reaction worksheets, questions, and revision for gcse combined science and chemistry. What happens to the concentrations of: A study of reaction _____ is called chemical _____.
Still another factor which can change a reaction’s rate is a catalyst. Web rates of reaction worksheets, questions, and revision for gcse combined science and chemistry. Rates of reaction, collision theory, effect of variables on reaction rates including temperature, concentration, pressure, surface area, catalysts, and inhibitors.note: Web worksheets are name per work reaction rates, chemistry 12 work 1 1, work.
According to the collision theory, what 3 circumstances are needed for c6h12o6 & o2 to react? A study of reaction _____ is called chemical _____. Reaction rate refers to how quickly or slowly the _____ disappear and the _____ appear. Web to summarise, the rate of reaction can be affected by: Web worksheets are name per work reaction rates, chemistry.
Web the rate of a chemical reaction is a measure of how fast a reaction takes place. Ii higher the temperature, the faster the reaction. I.e., how fast reactants are converted into products. Web rates of reaction teaching resources. Includes answers for marking in class.
The greater the frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles, the greater the reaction rate. C6h12o6 & o2 as the reaction proceeds ? If a reaction is to occur, reacting particles must first _____ and this _____ must be effective. Worksheet on rates of reaction key words, graphs and definitions. (1) temperature, (2) particle size, and (3) concentration of the.
Reaction Rates Worksheet - Provide definitions for the following terms; How will the rate change if the concentration of a is halved? C6h12o6 (s) + 6 o2(g) 6 h2o (g) + 6 co2 (g) 1. Ii higher the concentration, the faster the reaction. For example, in a reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid, the rate could be measured in terms of the change in concentration of the hydrochloric acid per second. The equation for the reaction is: (1) temperature, (2) particle size, and (3) concentration of the reactants. Still another factor which can change a reaction’s rate is a catalyst. Also includes a rag table to help pupils identify which sheet will help them progress. Worksheets and lesson ideas to challenge students to think hard about rates of reaction, graphs and collision theory (gcse and key stage 3) rates of reaction is a rich topic area for practicals that students really enjoy.
Ii higher the temperature, the faster the reaction. Use this reaction for the questions below: Web the rate of a chemical reaction is a measure of how fast a reaction takes place. A reaction has the experimental rate law, rate = k[a]2. Another article, rationalising rates, includes tips for teaching rates of reaction using graphs.
The greater the frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles, the greater the reaction rate. Includes answers for marking in class. What happens to the concentrations of: Web a range of worksheets, with answers, to help pupils to revise aspects of rates of reaction, including:
I have used other people's resources for one of the questions, thanks to them. Web a range of worksheets, with answers, to help pupils to revise aspects of rates of reaction, including: A reaction has the experimental rate law, rate = k[a]2.
Web rates of reaction teaching resources. Web chemical kinetics is the study of the rates of chemical reactions; Web a student investigated the rate of reaction between calcium carbonate (marble chips) and hydrochloric acid.
Reaction Rate Refers To How Quickly Or Slowly The _____ Disappear And The _____ Appear.
Web calculating rates of reaction. Experimentally determined rate law expressions show how the rate of a reaction. The greater the frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles, the greater the reaction rate. (1) temperature, (2) particle size, and (3) concentration of the reactants.
It Is Measured In Terms Of The _____ Of The Reactants.
Ii higher the concentration, the faster the reaction. Worksheets and lesson ideas to challenge students to think hard about rates of reaction, graphs and collision theory (gcse and key stage 3) rates of reaction is a rich topic area for practicals that students really enjoy. B i a + c. For example, in a reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid, the rate could be measured in terms of the change in concentration of the hydrochloric acid per second.
It Is Defined As The Change In Concentration Of A Reactant Or Product Per Unit Time.
I have used other people's resources for one of the questions, thanks to them. 18 mean rate of reaction = quantity of product formed time taken mean rate of reaction = 30 15 Web to summarise, the rate of reaction can be affected by: Answer the following questions using complete sentences (a and b);
All Your Revision In One Place.
I.e., how fast reactants are converted into products. Example questions from the worksheet: Part of combined science the. H2o + co2 as the reaction proceeds ?