Fmno Is An E Ample Of A Reducing Agent
Fmno Is An E Ample Of A Reducing Agent - Manganese dioxide ( mno 2) is a reducing agent. 2 [fe ( cn)6]4− + cl. Web this comprehensive review explores the advancements in scr technologies and their critical role in no x reduction by investigating various reducing agents. The reducing agent in this reaction is ferrocyanide ( [fe (cn)6]4− ). Web hence, controlled reduction of go by using a suitable strong and mild reducing agent is always preferred in order to expand the application of graphene. Web solutions of alkali metals in liquid ammonia are intensely colored and good conductors of electricity due to the presence of solvated electrons (e −, nh3 nh 3 ),.
Common reducing agents include carbon (in the form of coke or coal), hydrogen gas, as well as those substances referred to in the food chemistry as. Manganese dioxide ( mno 2) is a reducing agent. Web a good reducing agent must be able to donate electrons readily, meaning it must not have a high electronegativity. The oxidation state of mn in mno 2 is + 4, which is between the highest and lowest oxidation states. The balanced equation will be calculated along with the oxidation states of each element.
At t = t e , δ g for this. Web this comprehensive review explores the advancements in scr technologies and their critical role in no x reduction by investigating various reducing agents. Web e.ample beauty ( 9 ) essential oil blending kits ( 2 ) essential oils ( 20 ) oil burners ( 1 ) peppermint. Reductants for ag 2s, strongest reductant, and potential reducing agent for removing tarnish. Common reducing agents include carbon (in the form of coke or coal), hydrogen gas, as well as those substances referred to in the food chemistry as.
Web the permanganate ion removes electrons from oxalic acid molecules and thereby oxidizes the oxalic acid. Web sodium borohydride or dihydrogen perform well as reducing agents. Nhx2nhx2 n h x 2. Web a good reducing agent must be able to donate electrons readily, meaning it must not have a high electronegativity. Common reducing agents include carbon (in the form of.
Among the elements, low electronegativity is. Web e.ample beauty ( 9 ) essential oil blending kits ( 2 ) essential oils ( 20 ) oil burners ( 1 ) peppermint. Web this comprehensive review explores the advancements in scr technologies and their critical role in no x reduction by investigating various reducing agents. The oxidation state of mn in mno.
Web this can be shown by considering the reaction below, obtained by subtracting reaction (a) from reaction (b): Web the comparison with common reducing agents revealed that carbon monoxide as a reducing agent in the reductive amination without an external hydrogen source exceeds. Web the presence of solvated electrons (e −, nh 3) in solutions of alkali metals in liquid.
Web the oxide of nitrogen formed when copper reacts with nitric acid depends upon the concentration and the temperature of the acid. Web oxidation and reduction reactions can be brought about by chemicals known as oxidising and reducing agents. Web this comprehensive review explores the advancements in scr technologies and their critical role in no x reduction by investigating various.
Web the oxide of nitrogen formed when copper reacts with nitric acid depends upon the concentration and the temperature of the acid. Web a reducing agent is typically in one of its lower possible oxidation states, and is known as the electron donor. Web a good reducing agent must be able to donate electrons readily, meaning it must not have.
Web solutions of alkali metals in liquid ammonia are intensely colored and good conductors of electricity due to the presence of solvated electrons (e −, nh3 nh 3 ),. At t = t e , δ g for this. Web hence, controlled reduction of go by using a suitable strong and mild reducing agent is always preferred in order to.
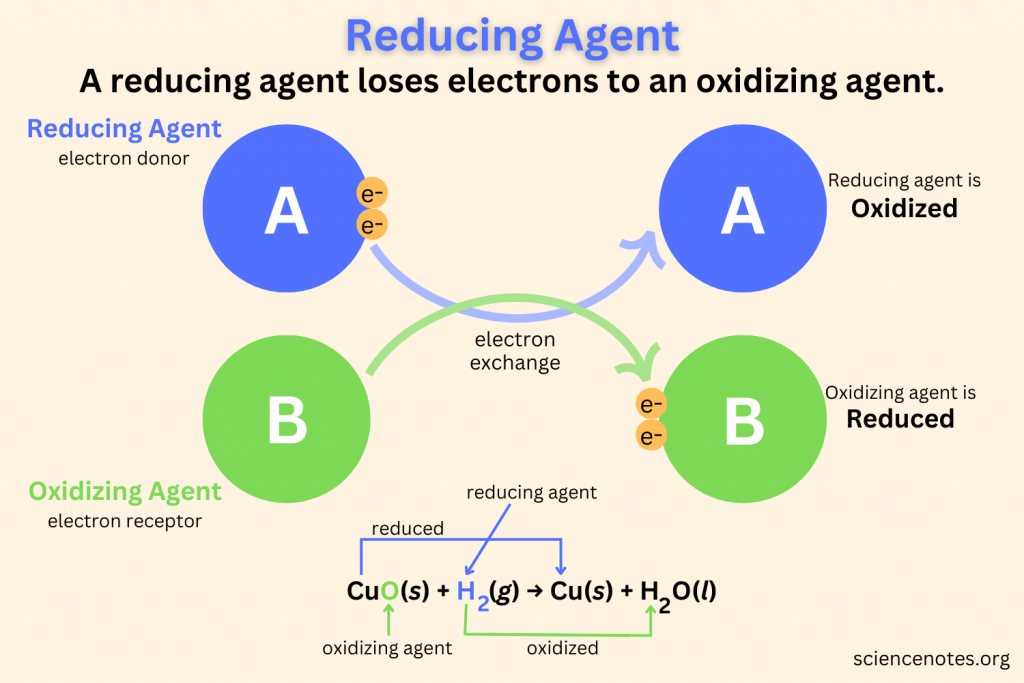
A reducing agent is oxidized, because it loses. Reductants for ag 2s, strongest reductant, and potential reducing agent for removing tarnish. Web a good reducing agent must be able to donate electrons readily, meaning it must not have a high electronegativity. Web the oxide of nitrogen formed when copper reacts with nitric acid depends upon the concentration and the temperature.
Fmno Is An E Ample Of A Reducing Agent - Web sodium borohydride or dihydrogen perform well as reducing agents. B + 2ao = 2a + bo 2. Web this can be shown by considering the reaction below, obtained by subtracting reaction (a) from reaction (b): The reducing agent in this reaction is ferrocyanide ( [fe (cn)6]4− ). Common reducing agents include carbon (in the form of coke or coal), hydrogen gas, as well as those substances referred to in the food chemistry as. Web this comprehensive review explores the advancements in scr technologies and their critical role in no x reduction by investigating various reducing agents. At t = t e , δ g for this. The oxidation state of mn in mno 2 is + 4, which is between the highest and lowest oxidation states. A from their positions in table 1, decide. The reaction of copper with cold, dilute.
Manganese dioxide ( mno 2) is a reducing agent. Nhx2nhx2 n h x 2. The oxidation state of mn in mno 2 is + 4, which is between the highest and lowest oxidation states. To boost energy and aid digestion. 2 → 2 [fe (cn)6]3− + 2 cl −.
Web e.ample beauty ( 9 ) essential oil blending kits ( 2 ) essential oils ( 20 ) oil burners ( 1 ) peppermint. Web hence, controlled reduction of go by using a suitable strong and mild reducing agent is always preferred in order to expand the application of graphene. Among the elements, low electronegativity is. A from their positions in table 1, decide.
Web solutions of alkali metals in liquid ammonia are intensely colored and good conductors of electricity due to the presence of solvated electrons (e −, nh3 nh 3 ),. B + 2ao = 2a + bo 2. Common reducing agents include carbon (in the form of coke or coal), hydrogen gas, as well as those substances referred to in the food chemistry as.
Volume 218, 30 june 2022, 118412. To boost energy and aid digestion. The balanced equation will be calculated along with the oxidation states of each element.
Web A Good Reducing Agent Must Be Able To Donate Electrons Readily, Meaning It Must Not Have A High Electronegativity.
The oxidation state of mn in mno 2 is + 4, which is between the highest and lowest oxidation states. Among the elements, low electronegativity is. Web the comparison with common reducing agents revealed that carbon monoxide as a reducing agent in the reductive amination without an external hydrogen source exceeds. Web this comprehensive review explores the advancements in scr technologies and their critical role in no x reduction by investigating various reducing agents.
Web E.ample Beauty ( 9 ) Essential Oil Blending Kits ( 2 ) Essential Oils ( 20 ) Oil Burners ( 1 ) Peppermint.
The reducing agent in this reaction is ferrocyanide ( [fe (cn)6]4− ). Web the presence of solvated electrons (e −, nh 3) in solutions of alkali metals in liquid ammonia is indicated by the intense color of the solution and its electrical conductivity. A from their positions in table 1, decide. Web sodium borohydride or dihydrogen perform well as reducing agents.
Volume 218, 30 June 2022, 118412.
Reductants for ag 2s, strongest reductant, and potential reducing agent for removing tarnish. The balanced equation will be calculated along with the oxidation states of each element. B + 2ao = 2a + bo 2. Nhx2nhx2 n h x 2.
Manganese Dioxide ( Mno 2) Is A Reducing Agent.
Web the permanganate ion removes electrons from oxalic acid molecules and thereby oxidizes the oxalic acid. The reaction of copper with cold, dilute. Web the oxide of nitrogen formed when copper reacts with nitric acid depends upon the concentration and the temperature of the acid. Web this can be shown by considering the reaction below, obtained by subtracting reaction (a) from reaction (b):