Drawing Scale Factor
Drawing Scale Factor - Learn more about how to find the scale factor, uses of scale factor, along with important tips and solved examples on scale factor. As the numbers in the scale get bigger, i.e. Draw a scaled drawing of the first side. When an object becomes larger as a result of the scale factor, this is referred to as enlargement. Web the original shape is 3 by 4 so we multiply those to find the area of 12 square units. Web this number is called the scale factor.
Maps use scale factors to represent the distance between two places accurately. For instance, a scale factor of 48 (or 1:48) indicates that one unit on the drawing represents 48 of the same units in real life. The sizes of the angles do not change. You could also say, 1 unit in the drawing is equal to 10 units in real life. We multiply every side length of a shape by the scale factor to enlarge it.
Web in order to interpret and produce scale drawings we need to know the scale factor and the actual lengths of the object. We'll learn that you can use a scale factor to make lengths bigger or smaller. The new shape has length of 3x2 (3 x the scale factor) and height of 4x2 (4 x the scale factor). Web a drawing at a scale of 1:10 means that the object is 10 times smaller than in real life scale, 1:1. To scale objects (drawing content) to reference:
20 x 12 = scale factor 240. Draw a scaled drawing of the first side. This means that every centimetre on the diagram represents 2 2 metres in real life. We will also learn how to use a scale factor to make scale drawings of geometric shapes. Using a scale factor to enlarge a shape.
Sal looks at a figure and a scale copy of the figure to determine what scale factor was used to create the scale copy. Web in order to interpret and produce scale drawings we need to know the scale factor and the actual lengths of the object. Web this resource gives children the opportunity to practise drawing scale factor shapes.
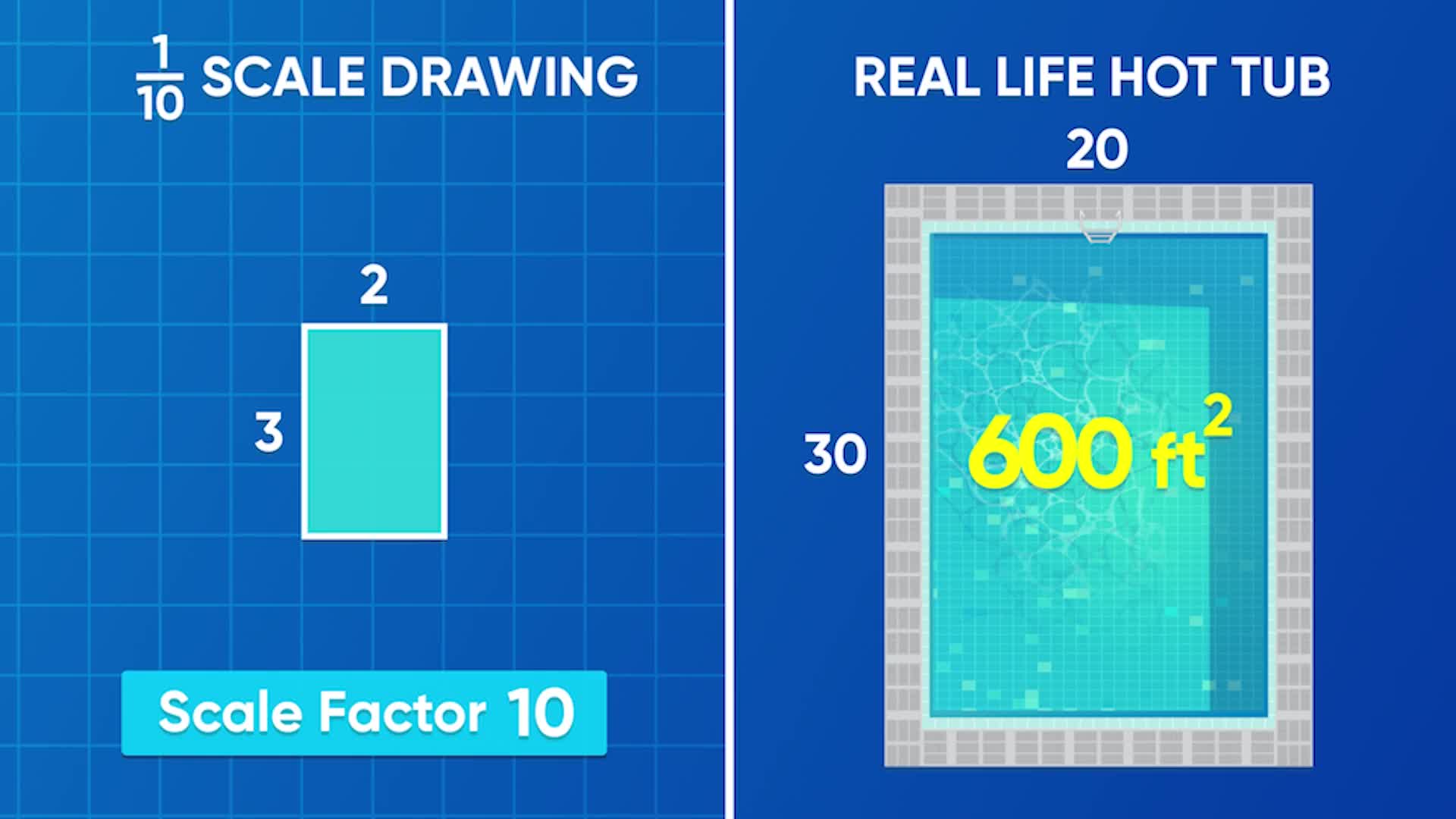
To scale objects (drawing content) to reference: This article will help you gain an intuitive understanding of cad scale factors and best practices for scaling design drawings. I confused why it must be 1:80 can it be 80:1. Shape a has been enlarged by scale factor 2 to give shape b. Below is a scale drawing of a pool with.
This article will help you gain an intuitive understanding of cad scale factors and best practices for scaling design drawings. Web a scale factor gives the ratio of the representation to the actual object. Web what is a scale factor? Web the original shape is 3 by 4 so we multiply those to find the area of 12 square units..
Web a drawing at a scale of 1:10 means that the object is 10 times smaller than in real life scale, 1:1. The dimensions of our scale drawing are 6 by 8 which gives us an area of 48 square units. Draw a scaled drawing of the first side. For instance, a scale factor of 48 (or 1:48) indicates that.
Web what is a scale factor? The dimensions of our scale drawing are 6 by 8 which gives us an area of 48 square units. Web how do you find the scale factor if two sides are missing and if the side that you are multiplying is also gone as well? A scale drawing is an accurate drawing of an.
Web this number is called the scale factor. This means that every centimetre on the diagram represents 2 2 metres in real life. How to use scale factor examples. Similar figures have the same shape but are of different sizes. The sizes of the angles do not change.
Drawing Scale Factor - What you will learn from this video. The scale factor is used to solve geometric problems. When an object becomes larger as a result of the scale factor, this is referred to as enlargement. Maps use scale factors to represent the distance between two places accurately. Web scale drawings (using scale factor) | generation genius. We will also learn how to use a scale factor to make scale drawings of geometric shapes. In the drawing that is not at 1:1 scale, find an object or line whose length you know. The lengths in a scale drawing are in proportion to the actual lengths of an object. What is a cad scale factor? Learn more about how to find the scale factor, uses of scale factor, along with important tips and solved examples on scale factor.
For instance, a scale factor of 48 (or 1:48) indicates that one unit on the drawing represents 48 of the same units in real life. Sal looks at a figure and a scale copy of the figure to determine what scale factor was used to create the scale copy. Web the original shape is 3 by 4 so we multiply those to find the area of 12 square units. Web this resource gives children the opportunity to practise drawing scale factor shapes on grids, measuring shapes and enlarging them by scale factors, as well as figuring out the measurements of shapes if they were enlarged by scale factors. 8/1 x 12 = scale factor 96.
For students between the ages of 11 and 14. The scale factor is used to solve geometric problems. To scale objects (drawing content) to reference: Sal looks at a figure and a scale copy of the figure to determine what scale factor was used to create the scale copy.
The lengths in a scale drawing are in proportion to the actual lengths of an object. The sizes of the angles do not change. Sal looks at a figure and a scale copy of the figure to determine what scale factor was used to create the scale copy.
For instance, a scale factor of 48 (or 1:48) indicates that one unit on the drawing represents 48 of the same units in real life. The scale factor is used to solve geometric problems. For students between the ages of 11 and 14.
We'll Learn That You Can Use A Scale Factor To Make Lengths Bigger Or Smaller.
As the numbers in the scale get bigger, i.e. Enlarge this shape by scale factor 2 2: Web the scale factor is the factor by which the dimensions of one figure need to be multiplied by in order to make the other figure. Web how do you find the scale factor if two sides are missing and if the side that you are multiplying is also gone as well?
For Students Between The Ages Of 11 And 14.
Similar figures have the same shape but are of different sizes. Sal looks at a figure and a scale copy of the figure to determine what scale factor was used to create the scale copy. Web this number is called the scale factor. A scale factor describes how much a shape has been enlarged.
Maps Use Scale Factors To Represent The Distance Between Two Places Accurately.
Lesson materials generate student link. When an object becomes larger as a result of the scale factor, this is referred to as enlargement. Using a scale factor to enlarge a shape. Web in order to interpret and produce scale drawings we need to know the scale factor and the actual lengths of the object.
Understand How A Scale Drawing Is Converted Into Real Numbers Using The Scale Factor.
The scale factor is used to solve geometric problems. This means that every centimetre on the diagram represents 2 2 metres in real life. How to use scale factor examples. Web explore how to write scales as ratios, and to use them to find measurements for scale drawings and real lengths with bbc bitesize maths.