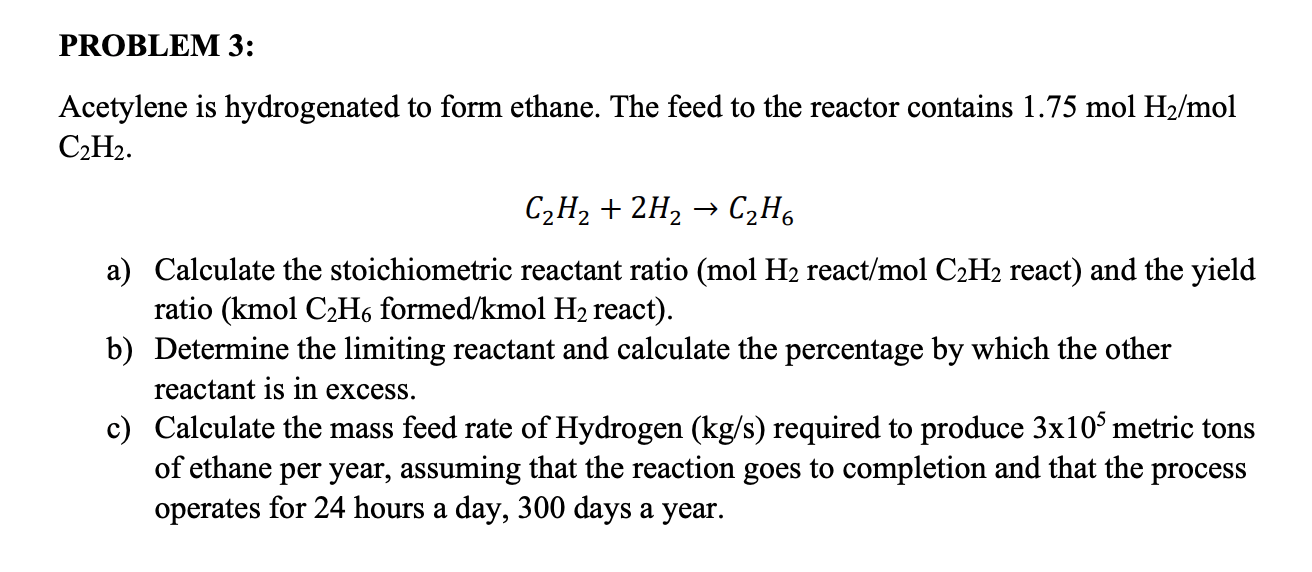
Acetylene Is Hydrogenated To Form Ethane
Acetylene Is Hydrogenated To Form Ethane - The feed to the reactor contains 1.40 mol h2/mol c2h2. The feed to the reactor contains 1.50 mol h2 /mol c2h2. (marks 20) acetylene (c2h2) is hydrogenated to form ethane (c2h6). C2h2 + 2h2 → c2h6 (a) stoichiometric ratio mol h2 react/mol c2h2 react = 2 mol h2 / 1 mol c2h2 yield ratio kmol c2h6formed/kmol h2 react = 1 kmol c2h6 / 2 kmol h2 (b) we have 1.50 mol h2/mol c2h2 ie. 1) calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio of hydrogen to acetylene (mol h2 /. Web hydrogenation of gas mixtures enriched in acetylene and hydrogen in which acetylene is not an impurity, but the main component that needs to be quantitatively converted into ethylene, is also of great scientific and practical interest.
The feed to the reactor contains 1.50 mol h2 /mol c2h2. Find all video solutions for your textbook. The reaction proceeds to completion. The feed to the reactor contains 1.40 mol h2/mol c2h2. The acetylides of silver, copper, mercury, and gold are detonated by heat, friction, or shock.
Write the stoichiometric equation for this reaction, and then answer the following questions: The reaction proceeds to completion. Calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol. The feed to thereactor contains 1.5 mol h2/mol c2h2.a. Web acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane in the following reaction c2h2 + 2h2 → c2h6.
The feed to the reactor contains 1.50 mol h_2/mol c_2h_2. Web hydrogenation of gas mixtures enriched in acetylene and hydrogen in which acetylene is not an impurity, but the main component that needs to be quantitatively converted into ethylene, is also of great scientific and practical interest. 0.7 mol h2 reacted/mol c2h2 reacted 0.5 mol c2hs formed/mol h2 reacted b..
C2h2 + 2h2 → c2h6 (a) stoichiometric ratio mol h2 react/mol c2h2 react = 2 mol h2 / 1 mol c2h2 yield ratio kmol c2h6formed/kmol h2 react = 1 kmol c2h6 / 2 kmol h2 (b) we have 1.50 mol h2/mol c2h2 ie. 0.7 mol h2 reacted/mol c2h2 reacted 0.5 mol c2hs formed/mol h2 reacted b. Find all video solutions.
The reaction proceeds to completion a. Calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol. Web acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane (c2h6). Conventional thermal hydrogenation routes require.
Web acetylene is hyrodgenated to form ethane. The feed to the reactor contains 1.50 mol h2/mol c2h2. Hydrogen (h2) is not in excess; 1) calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio of hydrogen to acetylene (mol h2 /. (marks 20) acetylene (c2h2) is hydrogenated to form ethane (c2h6).
Calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol h2 react/molc2h2 react) and the yield ration (. Web write the balanced equation for the reaction of acetylene and hydrogen to form ethane. (a) calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol h2 react/mol c2h2 react) and the stoichiometric yield ratio (kmol c2h6 formed/kmol h2 react). The reaction proceeds to completion. Web acetylene is hydrogenated to.
The feed to the reactor contains 1.50molh2/molc2h2 1.50 m o l h 2 / m o l c 2 h 2. The feed to the reactor contains 1.50 mol h2 /mol c2h2. The reaction proceeds to completion. Web acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. The feed to the reactor contains 1.50 \mathrm {mol} \mathrm {h}_ {2} / \mathrm {mol} 1.50molh2/mol.
0.7 mol h2 reacted/mol c2h2 reacted 0.5 mol c2hs formed/mol h2 reacted b. The feed to the reactor contains 1.50 mol h_2/mol c_2h_2. (a) calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol h2 h 2 react/mol c2h2 c 2 h 2 react) and the yield ratio (kmol c2h6 c 2 h 6 formed/kmol h2 h 2 react. Write the stoichiometric equation for.
Acetylene Is Hydrogenated To Form Ethane - In chemical reactions, the limiting reactant is the reactant that is completely consumed and determines when the reaction stops. 1) calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio of hydrogen to acetylene (mol h2 /. Calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol. Calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol h2 reacted/mol c2h2 reacted) and the yield ratio (mol czhs formed/mol h2 reacted). Web over fe 2 o 3 cluster, the overall barriers for h 2 dissociation, addition reaction of two hydrogen atom are respectively 26.6, 32 and 31.8 kcal·mol −1 during the acetylene hydrogenation to form ethylene and 26.5, 35.5 and 9.1 kcal·mol −1 for its further hydrogenation to produce ethane. Web hydrogenation of gas mixtures enriched in acetylene and hydrogen in which acetylene is not an impurity, but the main component that needs to be quantitatively converted into ethylene, is also of great scientific and practical interest. Write the stoichiometric equation for this reaction, and then answer the following questions: The feed to the reactor contains 1.50 \mathrm {mol} \mathrm {h}_ {2} / \mathrm {mol} 1.50molh2/mol \mathrm {c}_ {2} \mathrm {h}_ {2} c2h2. Web acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. The feed to thereactor contains 1.5 mol h2/mol c2h2.a.
Web the limiting reactant in the hydrogenation of acetylene to ethane, with feed containing 1.4 mol h2/mol c2h2, is acetylene (c2h2). Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane (c2h6). Web the hydrogen atoms in acetylene can be replaced by metallic elements to form acetylides—e.g., acetylides of silver, copper, or sodium. Web acetylene is hyrodgenated to form ethane. C2h2 + 2h2 → c2h6 (a) stoichiometric ratio mol h2 react/mol c2h2 react = 2 mol h2 / 1 mol c2h2 yield ratio kmol c2h6formed/kmol h2 react = 1 kmol c2h6 / 2 kmol h2 (b) we have 1.50 mol h2/mol c2h2 ie.
Web acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. The feed to the reactor contains 1.50 \mathrm {mol} \mathrm {h}_ {2} / \mathrm {mol} 1.50molh2/mol \mathrm {c}_ {2} \mathrm {h}_ {2} c2h2. The feed to the reactor contains 1.30 mol h2/mol c2h2. The feed to the reactor contains 1.40 mol h2/mol c2h2.
Web acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. Find all video solutions for your textbook. Web the limiting reactant in the hydrogenation of acetylene to ethane, with feed containing 1.4 mol h2/mol c2h2, is acetylene (c2h2).
Web acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. The feed to the reactor contains 1.50 mol h2/mol c2h2. Acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane (c2h6).
It Is Deficient By 30%.
1) calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio of hydrogen to acetylene (mol h2 /. Web acetylene is hyrodgenated to form ethane. Web acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane in the following reaction c2h2 + 2h2 → c2h6. Web acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane.
The Reaction Proceeds To Completion.
1) calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio of hydrogen to acetylene (mol h2 /. Web acetylene is hydrogenated to form ethane. (a) calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol h2 react/mol c2h2 react) and the stoichiometric yield ratio (kmol c2h6 formed/kmol h2 react). Find all video solutions for your textbook.
Web Four Types Of Behavior Have Been Distinguished:
Web chemistry questions and answers. Calculate the stoichiometric reactant ratio (mol h2. Web the limiting reactant in the hydrogenation of acetylene to ethane, with feed containing 1.4 mol h2/mol c2h2, is acetylene (c2h2). The feed to the reactor contains 1.50 mol h2/mol c2h2.
Web Acetylene Is Hydrogenated To Form Ethane In The Following Reaction C2H2 + 2H2 †’ C2H6.
C2h2 + 2h2 → c2h6 (a) stoichiometric ratio mol h2 react/mol c2h2 react = 2 mol h2 / 1 mol c2h2 yield ratio kmol c2h6formed/kmol h2 react = 1 kmol c2h6 / 2 kmol h2 (b) we have 1.50 mol h2/mol c2h2 ie. Web write the balanced equation for the reaction of acetylene and hydrogen to form ethane. The feed to the reactor contains 1.50 mol h2 /mol c2h2. We have the balanced reaction as follows: